Calibrating APSIM for forage sorghum using remote sensing and field data under sub-optimal growth conditions
Abstract
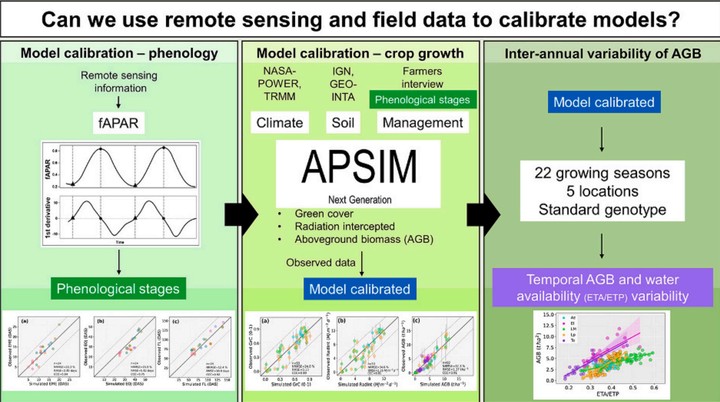
Mechanistic sorghum models have been mostly used to estimate sorghum yield for grain sorghum for a range of genotype, management, and environmental conditions. There is a lack of model testing for crop growth and development responses for forage genotypes and information for phenological parameterization under sub-optimal water and nitrogen stress conditions in forage systems. The aims of this study were to (i) use NDVI to parametrize APSIM model to estimate forage sorghum phenology, (ii) calibrate APSIM to simulate green cover, intercepted solar radiation and aboveground biomass, and (iii) quantify the variance of inter-annual aboveground biomass and the effect of water availability on forage sorghum biomass under sub-optimal environment × management combinations. We used climate, soil, management records and sorghum crop observations collected from farm and field experiments in Argentina and Australia. NDVI values were gathered from Sentinel-2 and a handheld optical sensor and then related to fAPAR measurements. Phenological stages were derived from fAPAR seasonal dynamics and implemented as input in the APSIM calibration. Finally, we assessed the temporal AGB variability through long-term simulations analysis. NDVI seasonal dynamics accurately represented the fraction of the absorbed photosynthetically active radiation (R2=0.92) and then, the remote-sensing parametrized APSIM model satisfactorily simulated crop phenology (CCC=0.75-0.92, NRMSE=9-22%). The model was also able to satisfactorily simulate crop growth (CCC=0.89 and NRMSE=24.8% for green cover; CCC=0.81 and NRMSE=34.6% for intercepted solar radiation; CCC=0.91 and NRMSE=37% for aboveground biomass). APSIM simulations during 22 years across 5 contrasting locations showed high inter-annual variability of aboveground biomass (CV=47%), mainly driven by inter-annual variation of soil water availability (CV=20%). Our study demonstrated that (i) remote sensing data was a reliable source for APSIM phenology parametrization, (ii) the model was able to satisfactorily simulate crop growth and development of forage sorghum under sub-optimal conditions across several genotype × environment × management combinations and (iii) water availability was the main driver of aboveground biomass inter-annual variance. Given the pressure of the global human population to satisfy an increasing demand for food, our results provide a new path for the combined use of remote sensing and mechanistic modelling to improve forage sorghum biomass estimations in marginal environments.